Seminar in Ecology
BIO605
Course information
BIO605 SEMINAR IN ECOLOGY
- Instructor: Akira Terui
- When: Thurs 12:30 – 14:45
- Where: Sullivan 349
- Virtual office hour: By appointment
- Required equipment: Laptop installed with R
What we will learn
What is Ecology?
- Term means “the study of the household”
- Ecologists study the interactions between organisms and their environment
What are the components of an organism’s environment?
- Physical conditions
- Chemical conditions
- Other organisms, both the same and different species
Topics
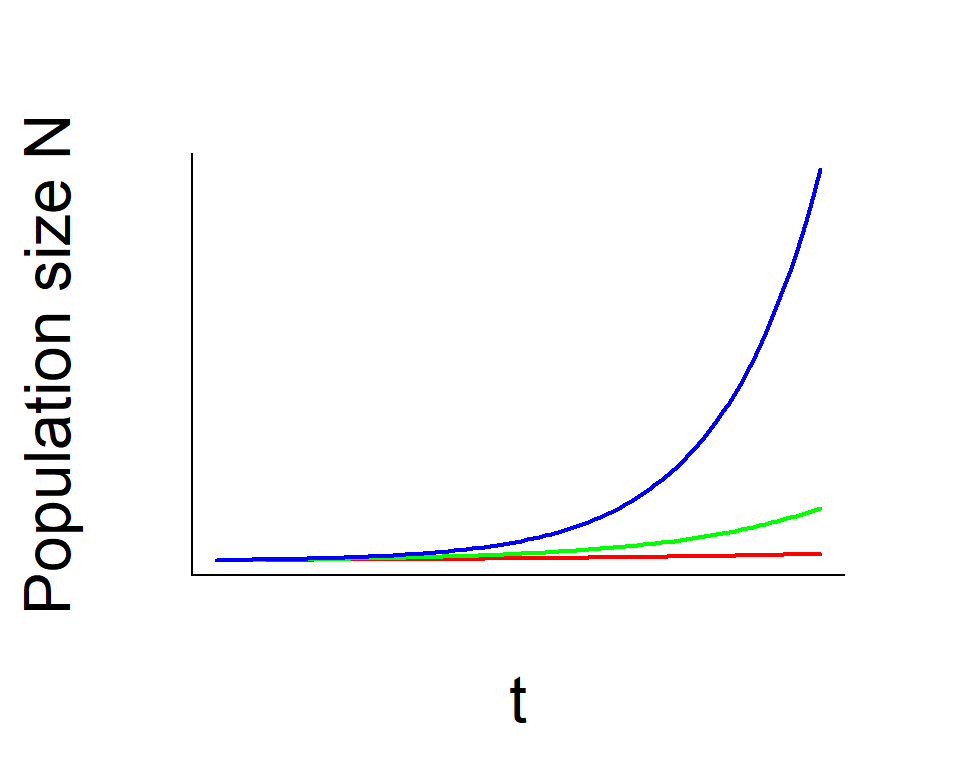
Population Ecology
- Population growth
- Density dependence
- Metapopulations
Community Ecology
- Competition
- Metacommunities
Food Web Ecology
- Diet estimate
- Food chain length
Theory & Observation
We learn theory, then expand
What is the role of theory in ecology?
What is the role of observation in ecology?

Theory
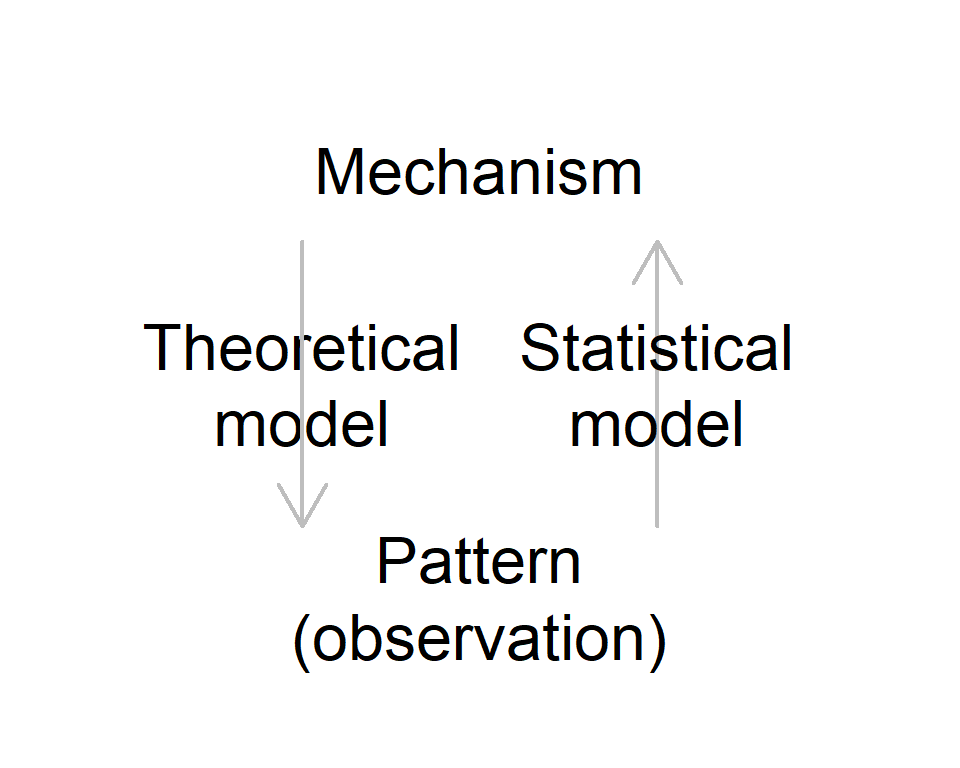
Theory
- Generate predictions with given mechanisms
- e.g. Do species A & B coexist if the two species compete for a common resource with strength \(\alpha\)?
Observation
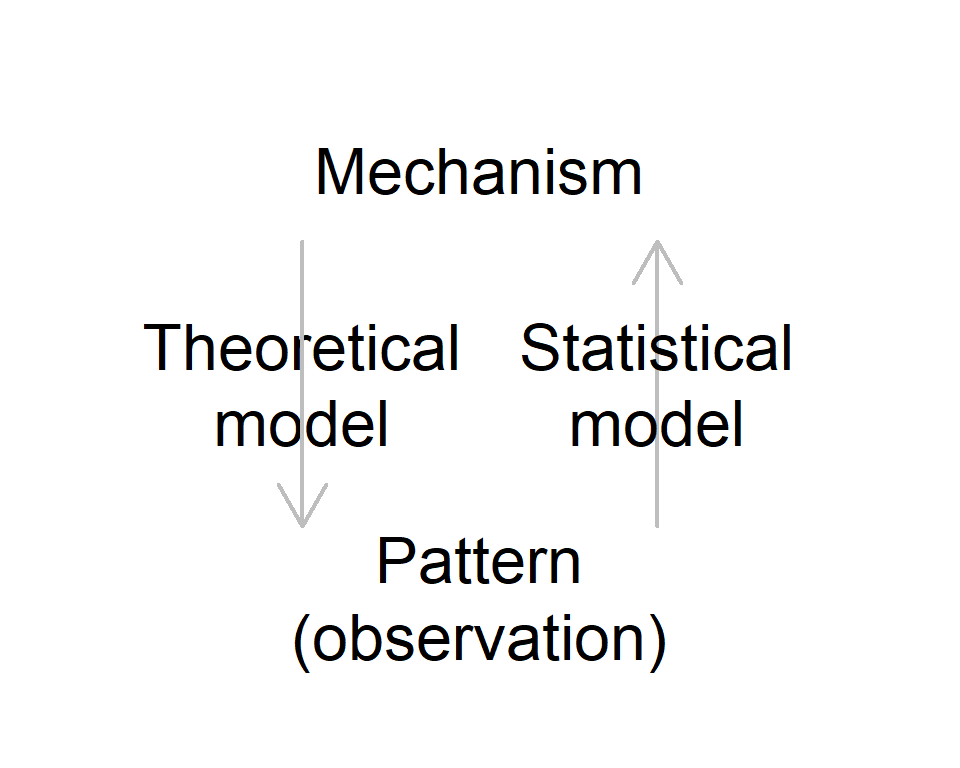
Observation
- Infer mechanisms with statistical modeling
- e.g. Species A does not co-occur with Species B - is this a result of competitive exclusion?
Theory has up- & downsides
Advantage
- Ultimate mode of experiment
- focus on a specific mechanism(s)
- exclude confounding influences
Disadvantage
- There are always assumptions
- These assumptions often oversimplify the nature (mathematical constraints)
- e.g., no immigration from other places etc.
Observation has up- & downsides
Advantage
- It’s real
- Reflect the full complexity of the nature
Disadvantage
- Multiple mechanisms can produce the same pattern
- Statistical approaches cannot separate these mechanisms, for example
- Species A does not co-occur with species B…
- Is this a result of competition or different environmental requirements?
Mismatch
Mismatch b/w theory & observation is common
- Theory often fail to explain observed patterns
- Motivate ecologists to develop new/novel concepts!
Course Structure
Part 1: Basic R exercise (Week 1 & 2)
- The first two weeks will be devoted to learning R
Part 2: Lecture & Paper discussion (Week 3 to 12)
- One lecture for each topic with R exercise
- Student-led paper discussion
Part 3: Synthesis (Week 13 & 14)
- Final report - synthesis questions
Grading
Attendance - Attendance - 10% - R script submission (lectures) - 30%
Paper Introduction
- Presentation evaluation - 15%
- Discussion participation (paper discussions) - 15%
Synthesis Paper/Presentation
- Synthesis report/presentation - 30%
Detailed guidelines will be provided!