ggbrnet
ggbrnet.RmdBasic usage
ggbrnet() is a wrapper of ggraph functions
for easy visualization of a network produced by brnet()
.
Patch color
Arguments: patch_color
Users can change how they color patches by specifying
patch_color. Default is "black". Other options
are env and disturb referring to the
environment and disturbance columns,
respectively:
## colored by `environment`
brnet() %>%
ggbrnet(patch_color = "env") + # "environment" works too
labs(color = "Environment")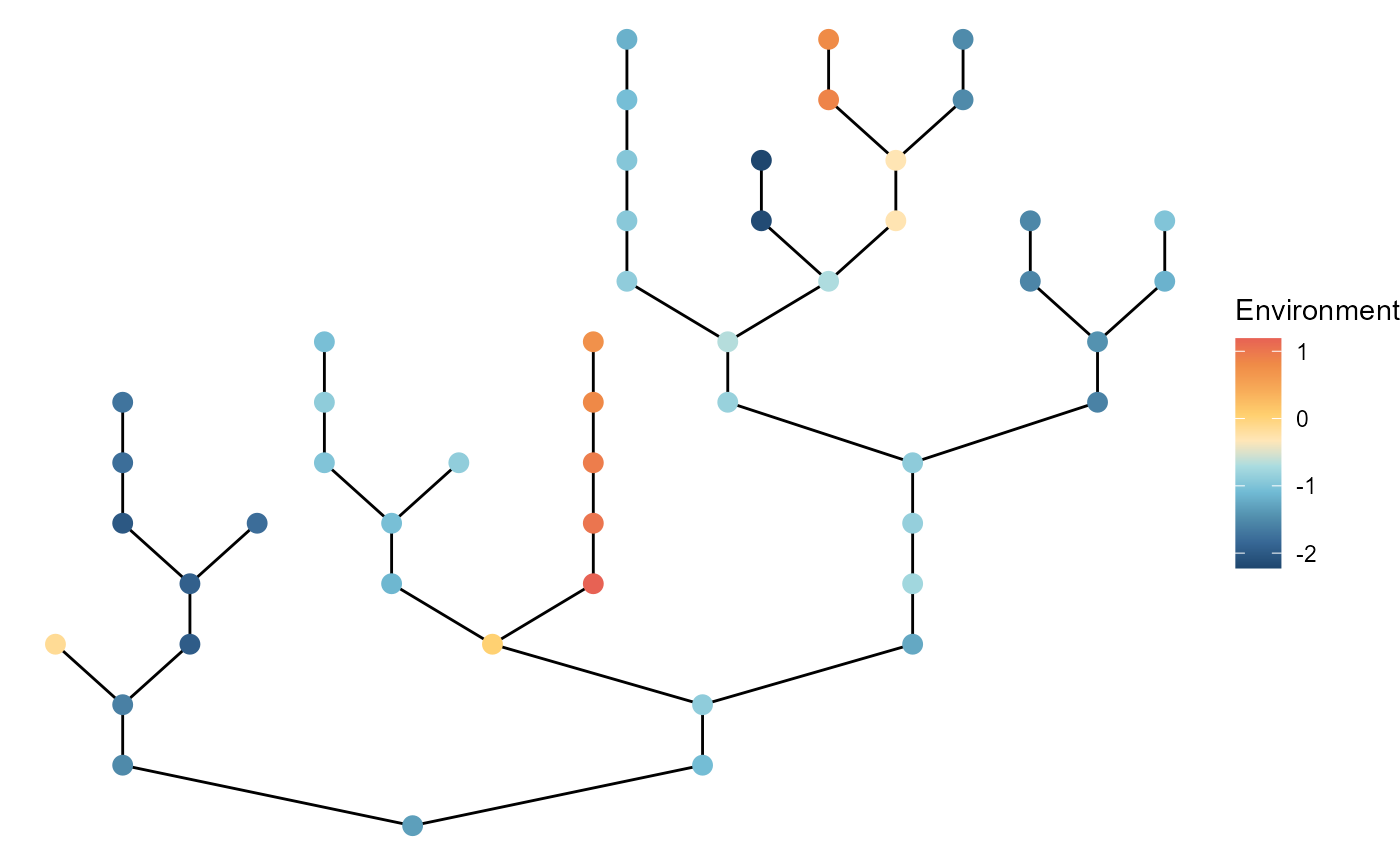
## colored by `disturbance`
brnet() %>%
ggbrnet(patch_color = "disturb") + # "disturbance" works too
labs(color = "Disturbance")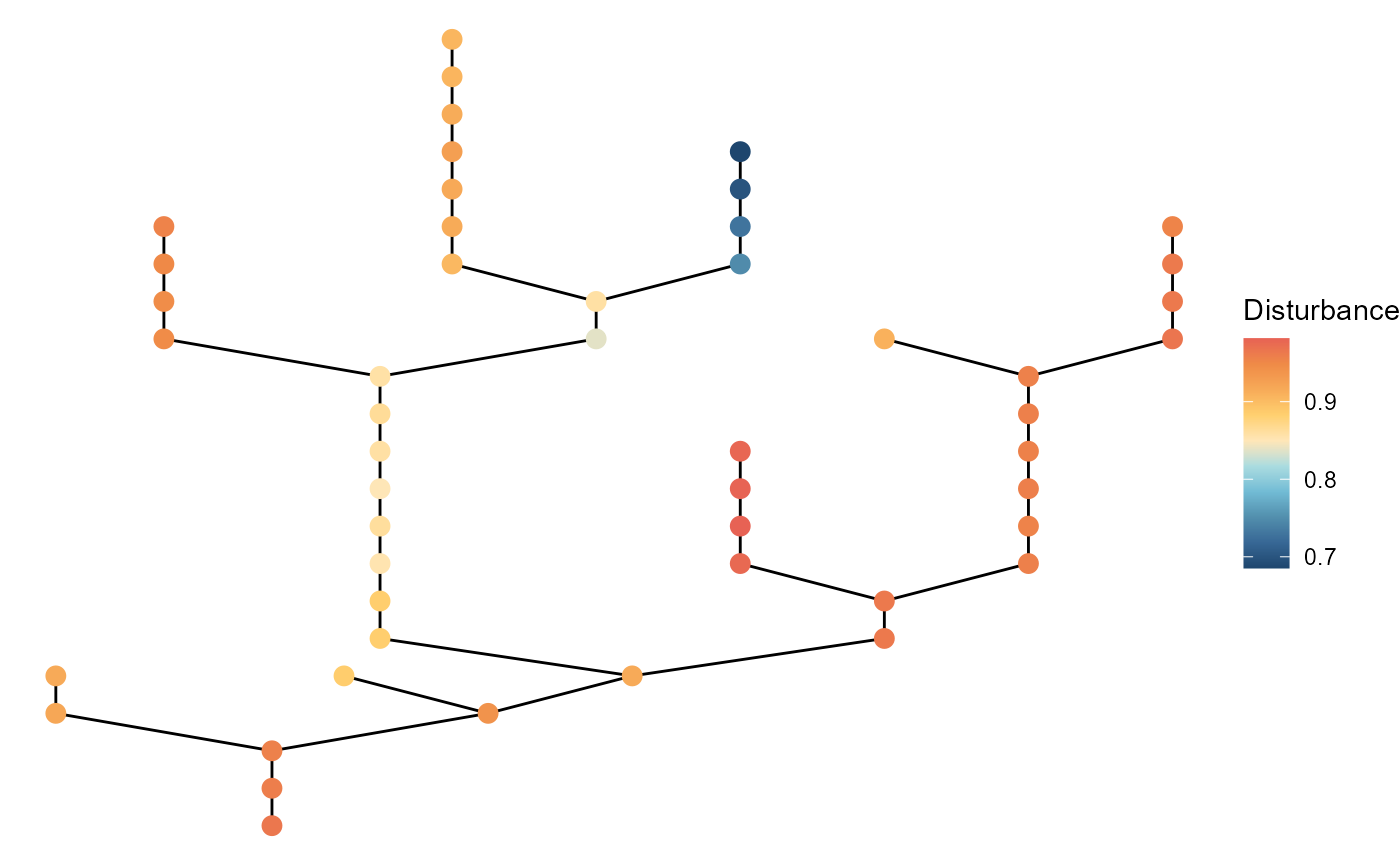
It is also possible to specify one of the columns in
.$df_patch:
df0 <- brnet()
df0$df_patch <- df0$df_patch %>%
mutate(x = runif(50, 0, 100))
df0 %>%
ggbrnet(patch_color = "x") +
labs(color = "x")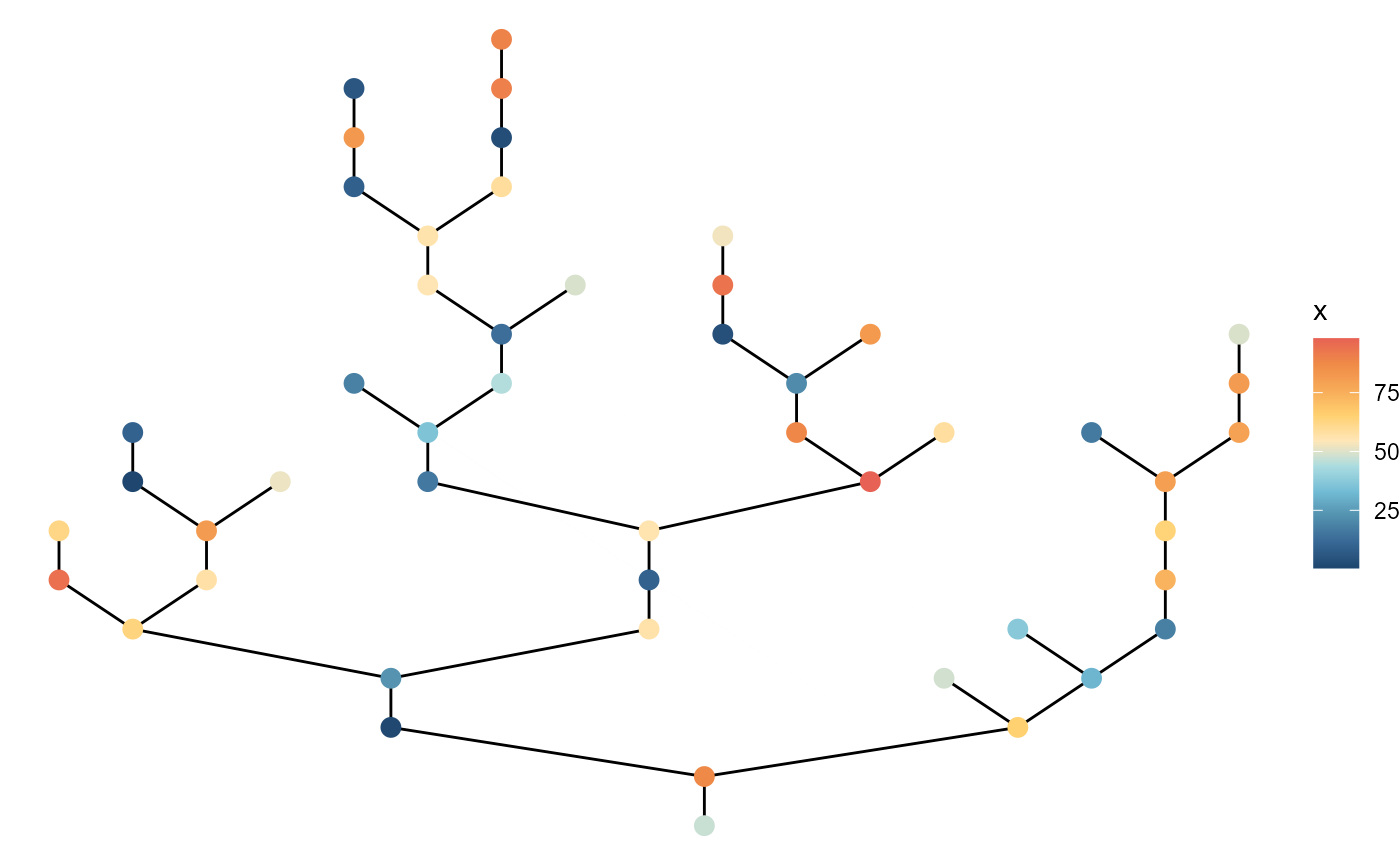
If patch_color is neither env,
disturb, nor any column in .$df_patch, the
function takes it as an ordinary color name, for example:
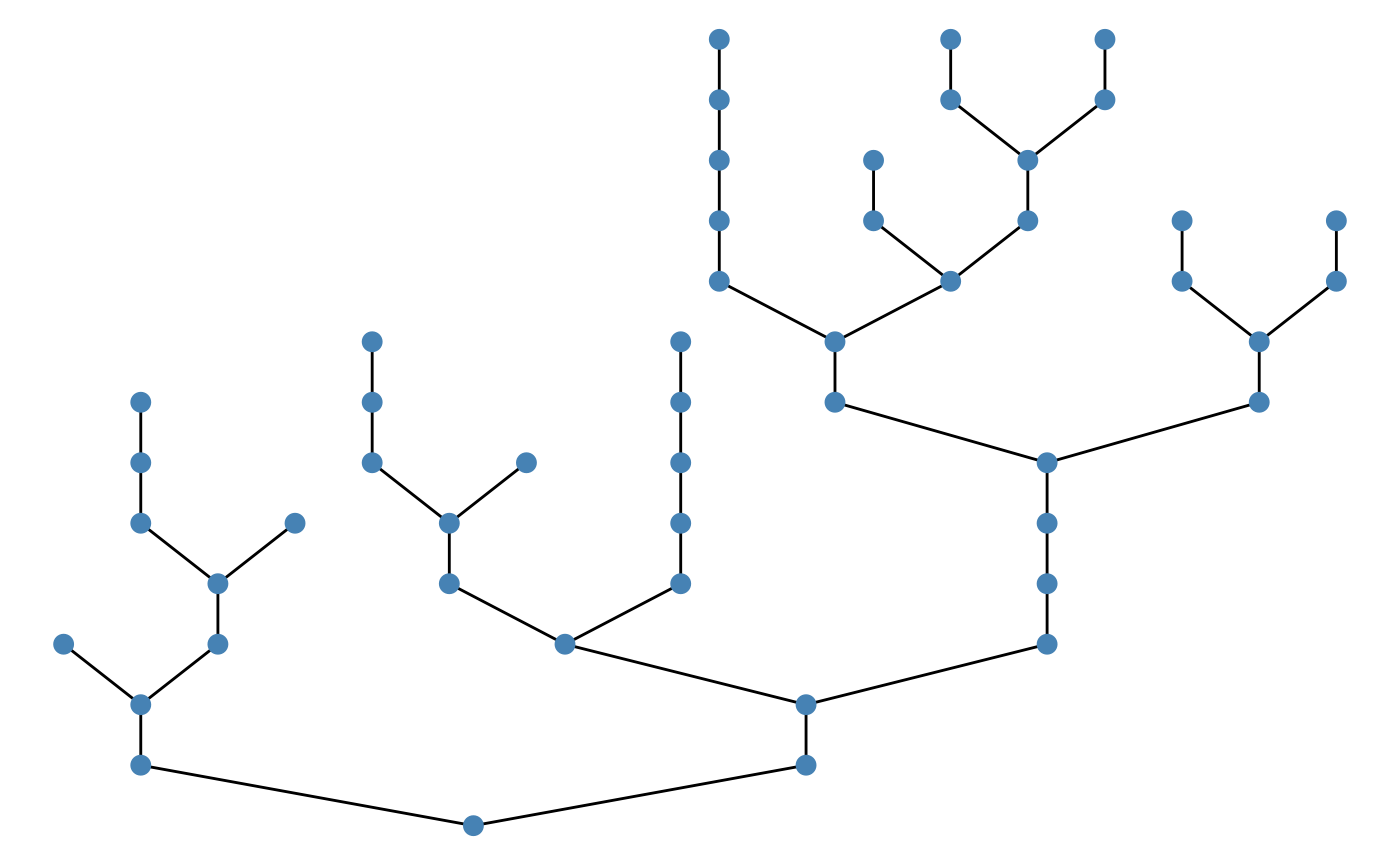
Patch label
Arguments: patch_label
Users may add patch labels using the argument
patch_label:
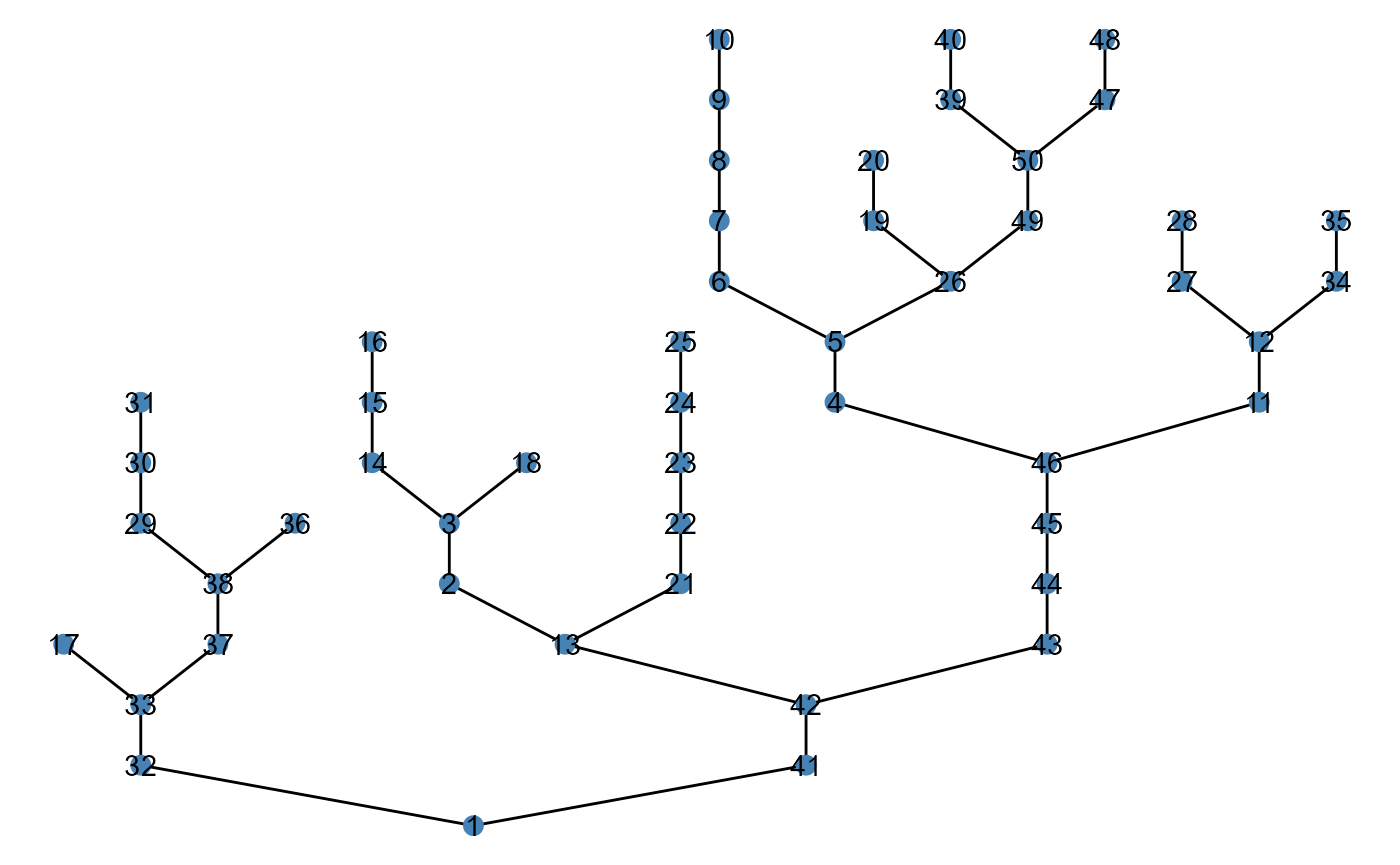


Users may specify additional arguments passed to
ggraph::geom_node_label() to tweak details, for
example: